Examining the Core Components of Electronic Systems
Electronic systems form the backbone of modern technology, powering everything from personal gadgets to complex industrial automation. Understanding the fundamental components that enable these systems to function is crucial for anyone interested in how digital devices operate. This article delves into the essential building blocks, from the physical hardware that processes information to the intricate software that dictates their behavior, providing insight into the innovation driving our connected world and the integration of various components.
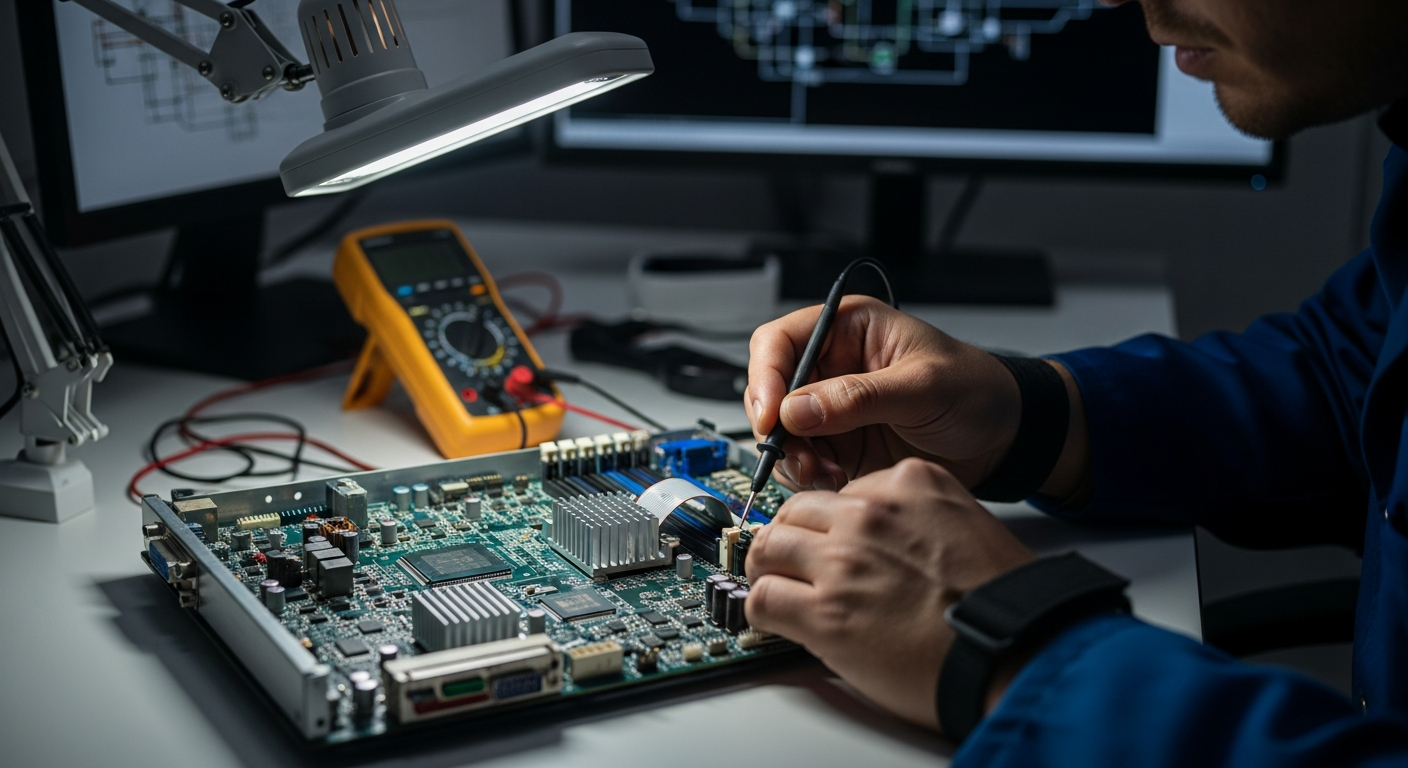
The intricate world of electronic systems is built upon a foundation of diverse components, each playing a vital role in the overall functionality of devices. From the smallest digital gadget to large-scale computing infrastructure, these systems are a testament to ongoing innovation in technology. Exploring these core elements helps demystify how our modern world is increasingly shaped by interconnected hardware and sophisticated software.
Understanding the Foundation: Hardware Components
At the heart of any electronic system lies its hardware, the tangible parts that enable its operation. These components include printed circuit boards (PCBs), resistors, capacitors, and various integrated circuits (ICs) that form the intricate circuits. The physical design and arrangement of these elements dictate the system’s capabilities and efficiency. From simple devices to complex computing platforms, the quality and design of hardware components are paramount to performance and reliability, directly influencing the speed and stability of data processing and overall system functionality.
The Brains of the Operation: Processors and Memory
Central to all modern electronics are processors and memory, often considered the ‘brains’ and ‘short-term memory’ of any digital system. Processors, such as Central Processing Units (CPUs) and Graphics Processing Units (GPUs), execute instructions and perform calculations at incredible speeds, driving all computing tasks. Memory, including Random Access Memory (RAM) and various forms of storage, provides the space for active data and programs. Together, these components facilitate rapid data access and manipulation, which is essential for multitasking and running complex applications, showcasing continuous innovation in silicon technology.
Facilitating Interaction: Displays and Peripherals
For users to interact with electronic devices, effective input and output mechanisms are essential. Displays, ranging from simple LED indicators to high-resolution screens, present visual information, making digital content accessible. Peripherals, such as keyboards, mice, touchpads, and sensors, allow users to input commands and data, bridging the gap between human intent and machine execution. These components are critical for user experience and are continuously evolving with new technology to offer more intuitive and immersive ways to engage with electronic systems and gadgets.
Connecting the Digital World: Networking and Connectivity
In an increasingly interconnected world, networking and connectivity components are indispensable. These elements enable electronic devices to communicate with each other and access broader networks like the internet. Wi-Fi modules, Ethernet ports, Bluetooth radios, and cellular modems facilitate seamless data exchange, supporting everything from local data sharing to global communication. The robust integration of these components ensures reliable connectivity, which is fundamental for modern digital systems, fostering global communication and data sharing across diverse platforms and devices.
The Invisible Force: Software and Digital Systems
While hardware provides the physical structure, software is the set of instructions that tells the hardware what to do. Operating systems manage hardware resources and provide a platform for applications, which are programs designed for specific tasks. Firmware, a type of software embedded directly into hardware, controls basic functions. The synergy between software and hardware is what brings electronic systems to life, enabling automation, complex data processing, and user interaction. Continuous advancements in software innovation drive new capabilities and efficiencies in all forms of computing.
Advancements in Integration and Automation
The ongoing evolution of electronic systems is characterized by increasing integration and automation. Components are becoming smaller, more powerful, and more interconnected, leading to highly integrated systems that can perform complex functions within compact devices. Automation, driven by sophisticated software and advanced sensors, allows systems to operate with minimal human intervention, enhancing efficiency and expanding capabilities across various industries. This trend signifies a shift towards smarter, more autonomous digital devices and systems that redefine how we interact with technology, from smart homes to industrial control systems.






